Hi, I hope you had a great day yesterday learning about the launch template and instances in EC2.
Today, we are going to dive into one of the most important concepts in EC2: Load Balancing.
What is Load Balancing..??
Load balancing is the process of distributing network traffic across multiple servers to ensure that no single server is overwhelmed with requests. The main purpose of load balancing is to improve the reliability, scalability, and performance of web applications by distributing traffic across multiple servers.
What is Elastic Load Balancing..?
Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) is a service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that automatically distributes incoming traffic across multiple EC2 instances. ELB provides three types of load balancers: Application Load Balancer (ALB), Network Load Balancer (NLB), and Classic Load Balancer (CLB).
By distributing traffic across multiple instances, ELB helps improve the reliability and availability of your applications, as well as their performance and scalability.
Elastic Load Balancing
AWS Load Balancers are virtual devices or services that distribute incoming network traffic across multiple targets, such as Amazon EC2 instances, containers, or IP addresses, to ensure your applications are highly available, fault-tolerant, and performant.
How Elastic Load Balancing Works

A load balancer accepts incoming traffic from clients and routes requests to its registered targets (such as EC2 instances) in one or more Availability Zones.
The load balancer also monitors the health of its registered targets and ensures that it routes traffic only to healthy targets. When the load balancer detects an unhealthy target, it stops routing traffic to that target. It then resumes routing traffic to that target when it detects that the target is healthy again.
Key Features & Benefits of Elastic Load Balancing
High Availability: Load balancers distribute traffic across multiple instances, reducing the risk of a single point of failure and ensuring high availability.
Auto Scaling: Load balancers can work with auto-scaling groups to automatically adjust the number of instances based on traffic load.
Security: Load balancers can act as a shield against distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks by providing protection and mitigation services.
SSL/TLS Termination: They can offload SSL/TLS encryption and decryption, reducing the processing burden on your backend instances.
Session Management: Some load balancers support session affinity, which ensures that a user's requests are consistently sent to the same backend instance.
AWS Load Balancer Types
There are four AWS load balancer types supported

Classic Load Balancer
Classic Load Balancer (CLB) is a legacy load balancer that is no longer recommended for new applications. It is a Layer 4 load balancer
Supports HTTP, HTTPS, TCP, and SSL listeners and supports sticky sessions using application-generated cookies.
AWS has announced that CLB will be deprecated on December 31, 2022.
Application Load Balancer
AWS Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes incoming traffic across
multiple targets, such as EC2 instances, containers, and IP addresses, in one or more Availability Zones.The Load Balancer distributes the traffic to the appropriate
Target Groups.New feature-rich,
layer 7load-balancing platform.Supports
web sockets, HTTP, HTTPS, microservices, and container-based applications, including deep integration with EC2 container service.Support for
path-based and host-based routing. Also, provide routing requests to multiple applications on a single EC2 instance.Cross-zone load balancingis always enabled and you can also specify Lambda functions are targeted to serve HTTP(S) requests.Supports load balancer-generated cookies only for sticky sessions.
Key Components of an Application Load Balancer:
Listeners: ALB uses listeners to check for connection requests from clients. These listeners are configured with specific protocols and ports and are at the forefront of routing decisions.
Rules: Listener rules define how the load balancer routes requests to its registered targets. Each rule consists of a priority, one or more actions, and conditions. Rules allow for sophisticated traffic management based on various factors.
Target Groups: These groups route requests to registered targets, such as EC2 instances, using specified protocols and port numbers. A target can be registered with multiple target groups, and health checks can be configured per target group

Network Load balancer
Network Load Balancer (NLB) shines as a high-performance solution designed to operate at the
transport layer (Layer 4)of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model.Connection baseload Balancing and it supports
TCP protocol.Support for static IP addresses for the load balancer. or assign one Elastic IP address per subnet enabled for the load balancer.
Cross-zone load balancing is disabled by default.
Key Components of a Network Load Balancer:
Listeners: NLB uses listeners to check for incoming connection requests from clients. Listeners are configured with specific protocols and ports, serving as the entry point for traffic.
Target Groups: These groups route incoming requests to registered targets, which can be EC2 instances or IP addresses. You can also configure target groups to support various protocols like TCP, UDP, TCP_UDP, and TLS, providing flexibility.

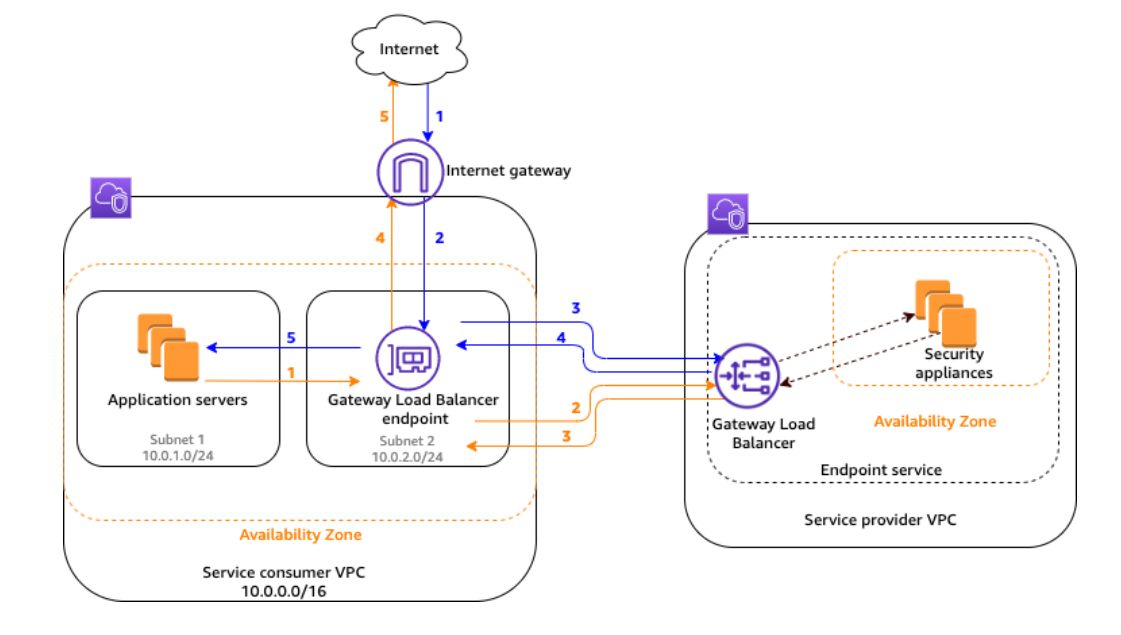
Gateway Load Balancer
Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) stands out as a specialized solution tailored for deploying and managing virtual appliances.
It makes it simple to scale, install, and manage your third-party virtual appliances.
Provide you with one gateway for distributing traffic across multiple virtual appliances, while scaling them up, or down, based on demand.
Gateway Load Balancer Endpoints:
- GWLB uses Gateway Load Balancer endpoints to securely exchange traffic across Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) boundaries